Factors Affecting Gender Ratios
There are a lot of factors that affect gender ratios across the country and around the world. Some of these factors include:
- Gender rates at birth
- Different mortality rates for males and females
- Effects of war
- Job Prospects (See North Dakota Oil Boom Affects Gender Ratios)
- Schools and Universities
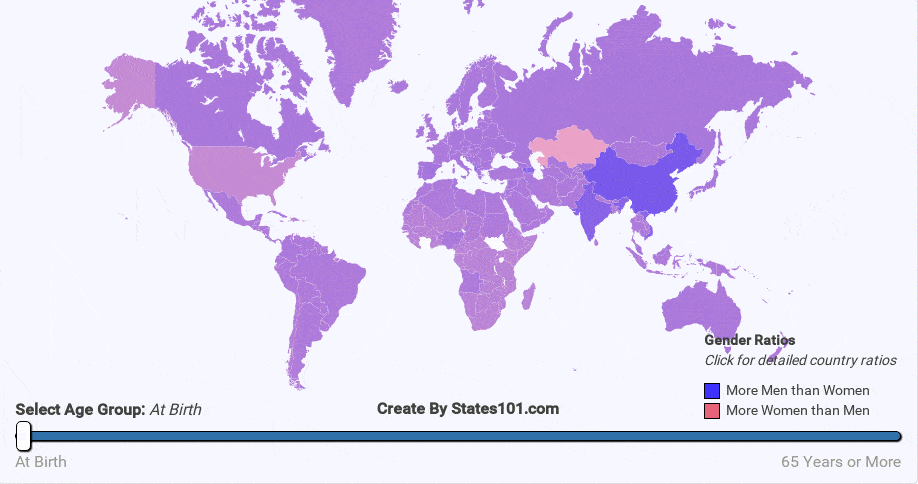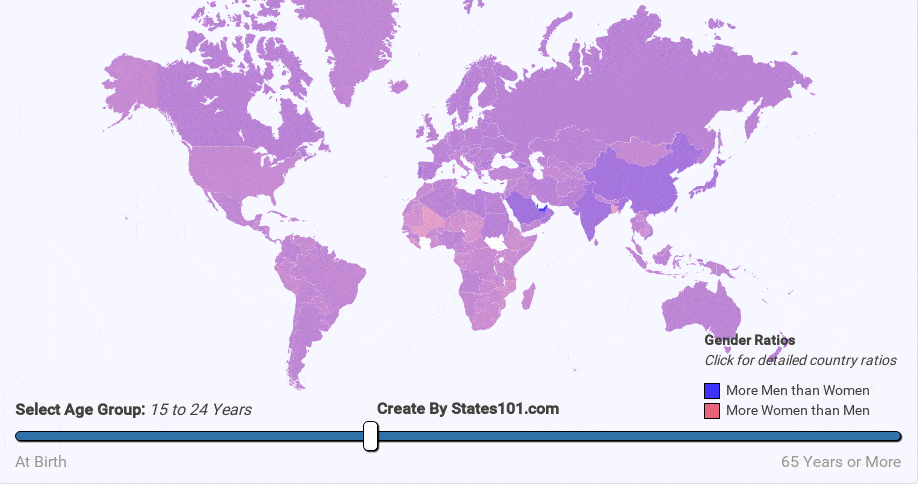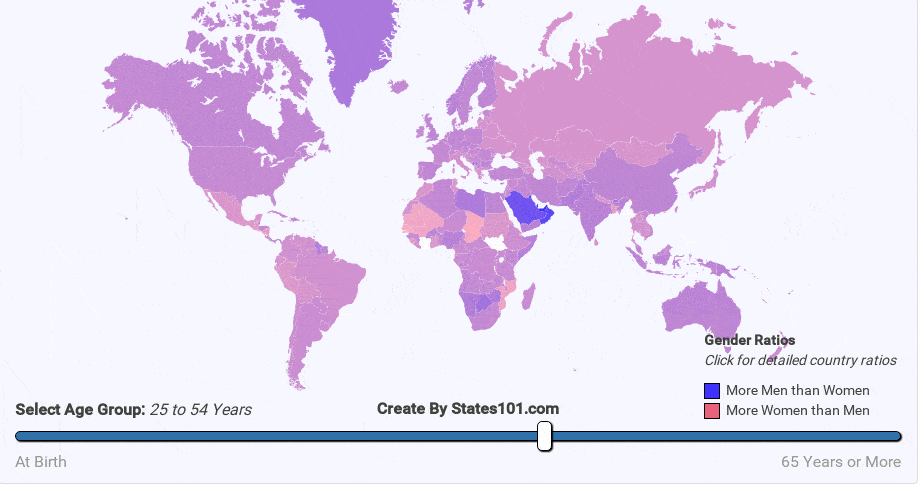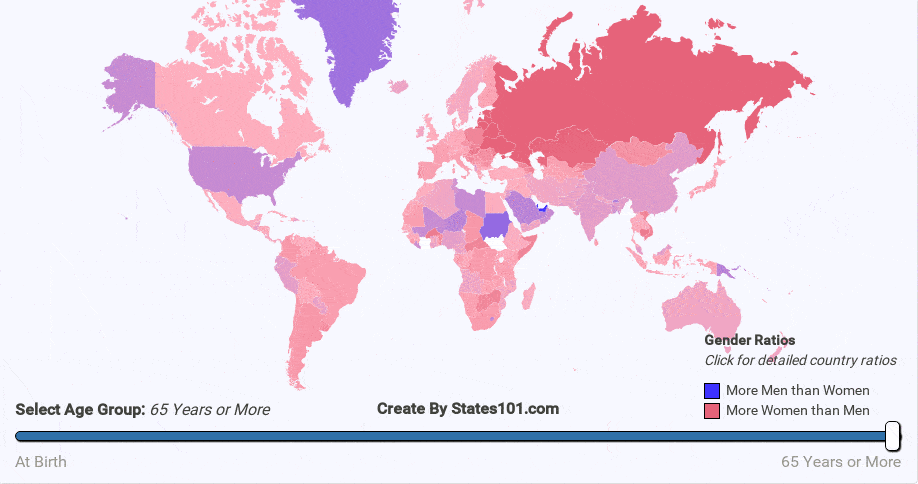
In all 50 states and every country in the world (except Kazakhstan), there are more males born than females. There are many theories to explain this phenomenon. Most people attribute the gender difference at birth to a natural way of balancing the fact that women tend to live longer.
Not only do women live long into their 80's and 90's than men, on average, but men are more likely to die early in life from a variety of hazards, such as:
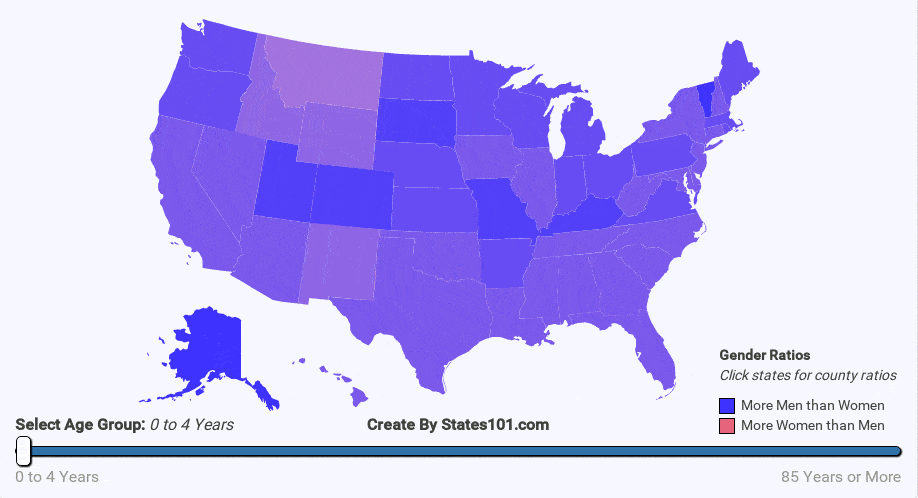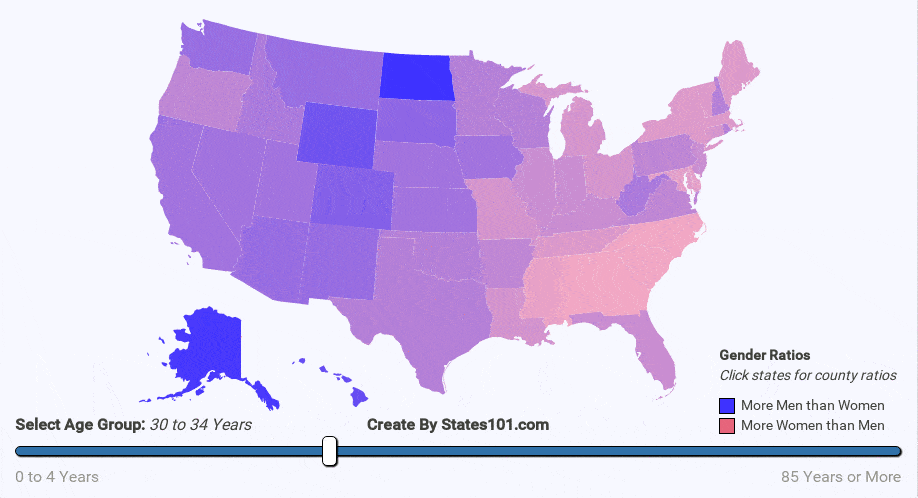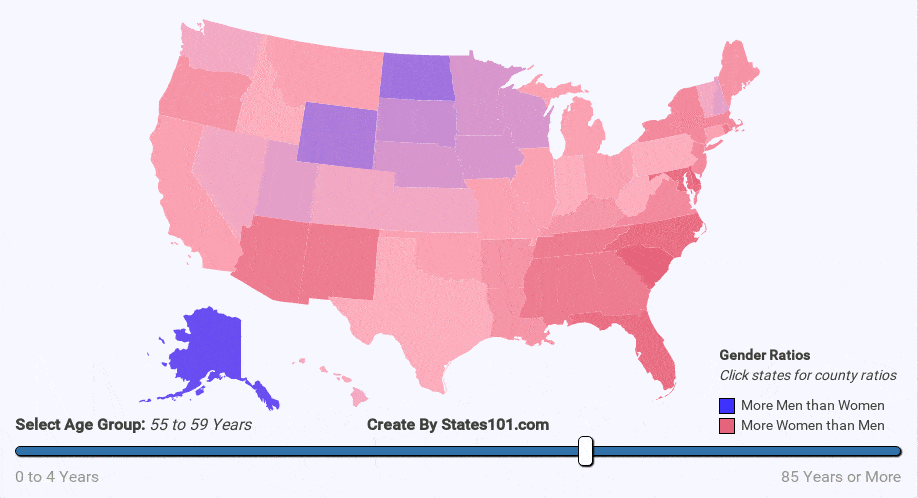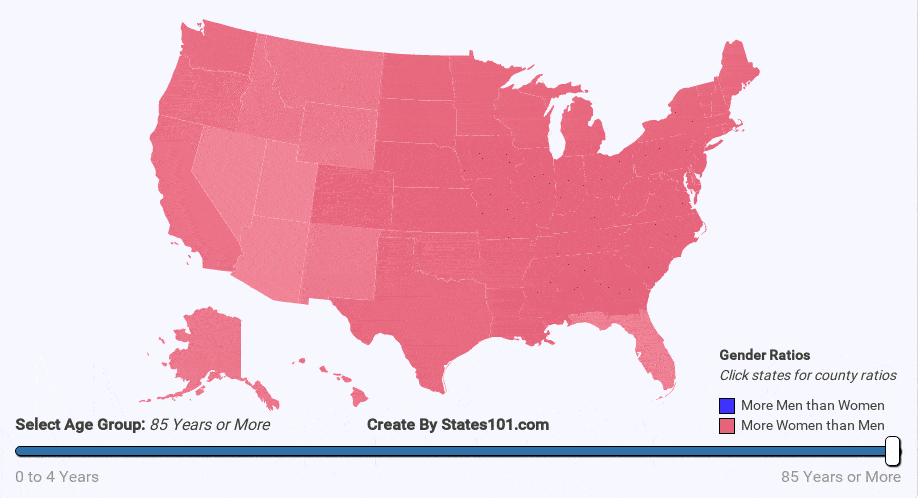
- war
- car accidents
- more risky behavior, in general
We can see the gender difference over time in the animations below. At birth, there are more males than females. But, that difference quickly corrects itself. By the age of 20-40 (depending on region) the gender rations are mostly equal (1 to 1). The cause is not exactly known, but it makes sense biologically for there to be an equal number of men and women at the age when most people reproduce. The gender ratio trend continues into old age. By the age of 60+, most regions have more women than men. By the age of 90, there are usually twice as many women as men.
In my research, I have not found a reason why only Kazakhstan has more females than males at birth. There very well may be a good explanation. If you have any information about this abnormality, please, contact us.
There are other interesting data points with explanations. For instance, you will notice a very high ratio (more males) in many Asian countries, especially China, Korea, and Japan. This is because in those cultures, people strongly prefer having a boy, rather than a girl. As a result, parents in these countries are more likely to keep a baby boy.
The effects of war can also be seen in the gender ratios map. War stricken countries like Mali, Zimbabwe, and Chad in Africa have a steep change in gender ratios for the 15 to 24 year old age group. This is likely because men are more likely to die in war than woman.
Job prospects also play a huge part in gender ratios. For instance, in Alaska, there are many more men than women. That is because there are more tough labor jobs that men are more likely to take in Alaska — jobs like King Crab Fisherman and Oil Drill Operator. This same effect can be seen in North Dakota where there are many typically-male jobs in the Shale Oil Drilling industry. Men more to these area in larger numbers than women. This skews the ratio in these regions.
Young people moving to cities have a huge effect on gender ratios on a city-by-city basis. But overall country and state ratios are largely unaffected. States101.com provides county-level gender ratio information in the United States. You will often see that more women than men live in counties with a major city such as New York and Washington D.C.
Texas is a great example of how gender ratios differ county-by-county. In Texas, you can see some counties have an overwhelming number of men. These counties are typically where oil drilling jobs are located. Counties in Texas where there are more females than males are counties where major cities and universities are located such as Dallas County and Bexar County, where San Antonia is located.
 States101
States101